Using the Global Unique Identifier System (GUID) for PPRL
The GUID is a Global Unique Identifier for each study participant that allows researchers to aggregate and share a participant’s data without exposing personally identifiable information (PII). The GUID is made up of random alpha-numeric characters and is not generated from PII/PHI.[1]
[1] Johnson SB, Whitney G, McAuliffe M, Wang H, McCreedy E, Leon Rozenblit L, Evans CC. Using Global Unique Identifiers to Link Autism Collections. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc., Vol. 17, No. 6, 689-695, 2010. PMCID: PMC3000750.
Note: Since the time of publication, the term GUID has taken on a more general meaning – “An implementation of the universally unique ID”. In the context of the BRICS system, the GUID process could now be better identified as a Privacy Preserving Record Linkage (PPRL) system. However, since the BRICS GUID system has been using the GUID term in documentation and software for more than a decade and it is familiar to our community, we will continue to use it for now.
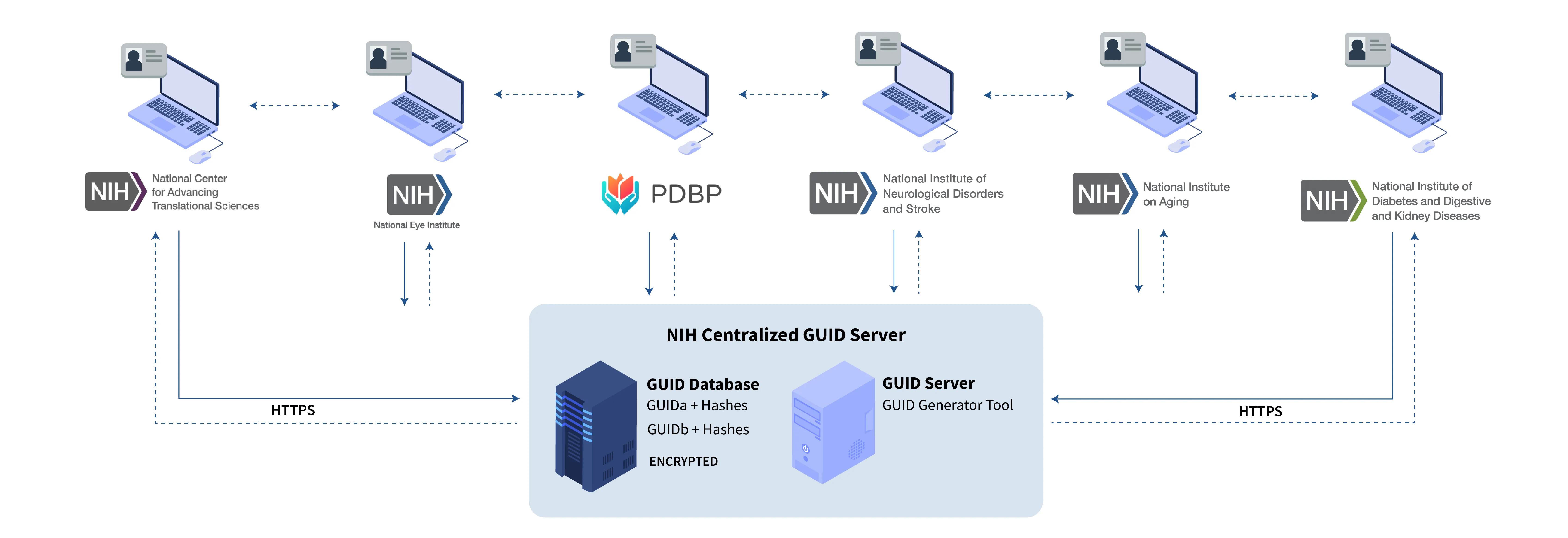
Institutes at NIH have successfully collaborated to develop a Multi-Tenant ‘Global Unique Identifier’ (GUID) solution for participant sharing across institutes and studies, known as the NINDS Centralized GUID solution.
- Management of study participants through the generation of a secure, random alphanumeric identifier (GUID)
- Mapping of study participants to study data for more efficient/comprehensive analysis
- Visibility to matching study participants/GUIDs across institutes and studies
- Collaboration amongst researchers to share study data (offline) about participants
The GUID process has two important attributes:
- PII is never sent to the BRICS system
- The GUID is a random number not generated from PII/PHI
In order to generate a GUID for a subject, the following PII is required:
- Complete legal given (first) name of subject at birth
- Complete legal additional name of subject at birth (If the subject has a middle name)
- Complete legal family (last) name of subject at birth
- Day of birth
- Month of birth
- Year of birth
- Name of city/municipality in which subject was born
- Country of birth
In order to generate a GUID for a subject, the following PII is optional:
- Physical sex of subject at birth
- Government Issued or National ID Number
- Country issuing Government-Issued or National ID